Britain's Electricity Generation - November 2024
16 December 2024
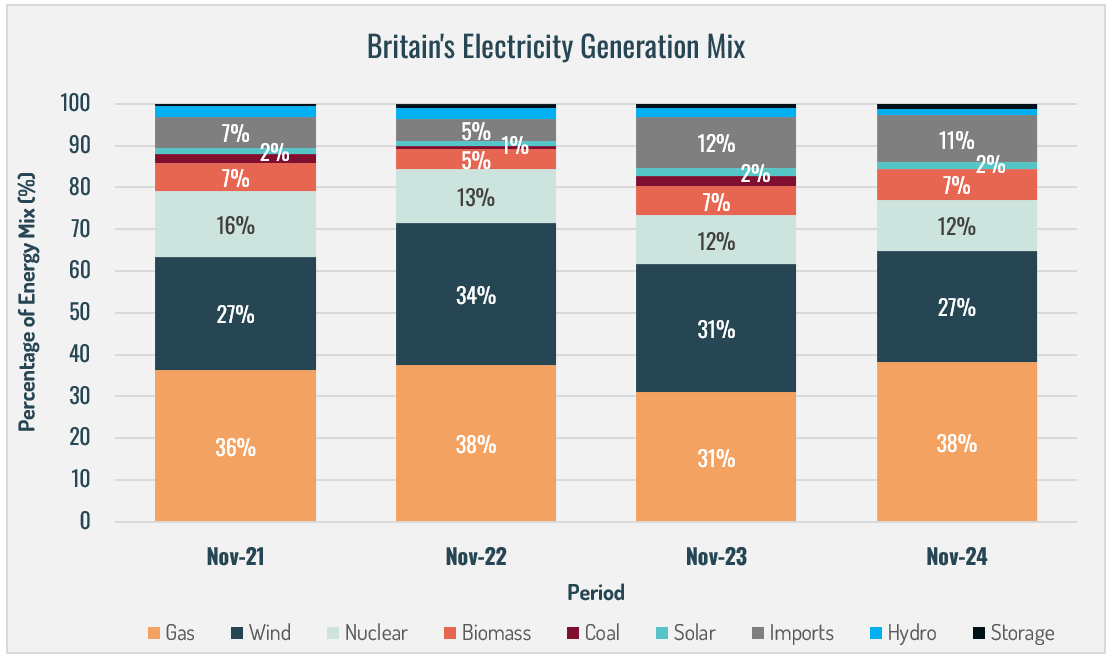
- In November 2024, gas was Britain's primary electricity source, accounting for 38% of the mix, a 7% increase from November 2023. Wind energy contributed 27%, 4% lower than the previous year, marking its lowest November share in four years.
- Nuclear, biomass, solar, and hydro maintained their contributions from 2023 at 12%, 7%, 2%, and 2%, respectively. Nuclear's share was 4% below November 2021, the lowest in four years. Coal contributed 0% after the closure of the last coal-fired power plant, Ratcliffe, in September, while imports provided 11%, the second-highest November level in four years.
- Zero-carbon sources made up 42% of Britain's electricity generation, the lowest for November in four years and 5% lower than last year. However, the rolling 12-month average for zero-carbon sources is 51%, the highest in the same period.
- The carbon intensity of electricity generation in November 2024 was 171 gCO₂/kWh, an increase of 6% from November in the previous year. The rolling 12-month average dropped to 124 gCO₂/kWh, marking a 21% reduction and the lowest level in four years, reflecting ongoing decarbonization efforts.
- Increasing the electricity generation from renewable sources can help achieve our net-zero ambitions, ensure energy security, and decrease reliance on imports.
Monthly Statistics
12-Month Rolling (Average) Statistics
To view our interactive renewables map,
click here
Data source: National Grid ESO 2024 (https://www.nationalgrideso.com/electricity-explained/electricity-and-me/great-britains-monthly-electricity-stats)

edenseven are following trends in the renewable energy sector closely, as decarbonising the energy sector is vital for ensuring a sustainable future and achieving Net Zero. Considering the recent DESNZ quarterly update of the renewable energy planning database, we have produced a consolidated summary of projects in the United Kingdom that have received planning permission. We will continue to release updates each quarter. INSIGHT Over the past 12 months, the UK approved 690 solar PV projects, 19% lower than the previous 12-month period. Despite the decline in project numbers, the total approved energy capacity rose by 16%, reaching the highest level for solar PV granted planning permission in any 12-month period over the last 16 years. Onshore wind approvals increased, with 46 projects granted permission, up by 28% year-on-year. However, the total energy capacity from these projects fell by 33%, and the average capacity per project dropped by 47%, reflecting a shift toward smaller-scale onshore developments in the last 12-months. Offshore wind saw a 67% increase in project approvals, with five projects granted permission. Yet, total energy capacity fell by 61%, and the average capacity per project declined by 77%, marking a significant reduction in project scale. In total, the combined approved energy capacity from solar PV, onshore wind, and offshore wind over the last 12 months reached 6,745 MW, ranking fourth-highest across the past 16 years.

In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors have moved from niche considerations to critical drivers of long-term value, investor confidence, and societal impact. Companies are increasingly recognising the imperative to address their environmental footprint, foster positive social contributions, and uphold robust governance standards. However, despite this growing awareness and investment, a significant hurdle remains for many organisations: the common misconception that ESG can simply be an add-on . Too often, we see ESG treated as a separate department, a compliance checklist, or merely a side project tacked onto existing operations. This "bolt-on" approach , while seemingly an easy entry point, is a primary reason why even well-intentioned ESG initiatives ultimately fail to deliver meaningful, transformative impact. When ESG isn't woven into the very fabric of a company's strategy, culture, and decision-making processes, it becomes just another isolated function, lacking the power and resources to drive real change and unlock genuine value. This article will delve into why this approach falls short and, more importantly, outline how a strategic, integrated approach to ESG can lead to tangible business outcomes and sustainable growth. The Challenge "We have a sustainability team of 3 people trying to transform a company of 10,000." This candid observation highlights the fundamental flaw in many organisations' approach to ESG. When ESG is treated as an isolated function, disconnected from the core business, it struggles to gain traction and deliver real transformation. Uncovering the Shortcomings of This Approach ESG treated as a separate function rather than core business strategy Sustainability goals disconnected from business objectives and KPIs Executive teams struggle to weave ESG into existing strategic planning processes ESG initiatives compete against business priorities instead of enabling them Lack of integration creates silos and limits transformation impact Solution Framework: Making ESG a Strategic Enabler What's The Solution? To move beyond the bolt-on approach, ESG must be strategically integrated into every facet of the business. This shift transforms ESG from a compliance burden into a powerful driver of competitive advantage and sustainable growth. This means businesses need to: Embed ESG considerations into annual strategic planning and budget cycles Align ESG materiality assessments with business risk and opportunity mapping Integrate sustainability metrics into core business dashboards and board reporting Make ESG performance criteria part of business unit strategy reviews Connect ESG goals to market expansion, operational efficiency, and innovation pipelines Train leadership teams on ESG as competitive advantage, not a compliance burden How edenseven Helps: Enabling Integrated ESG Strategies Are your ESG efforts feeling disconnected and underperforming? edenseven closes the gap between ambition and execution. We combine deep technology understanding with real-world market experience to empower companies to not just meet climate goals, but to achieve sustainable, profitable growth . We design bespoke, data-driven sustainability strategies that are fully integrated into your core business, turning ESG into a powerful strategic enabler that unlocks new opportunities and mitigates risk, rather than a costly, isolated add-on. If you would like to find out more about how we can deliver powerful ESG strategies for your organisation, send us a message today!

Fuel Type Breakdown Britain’s electricity generation in May 2025 was led by wind, which contributed 27% of the energy mix, its highest May share in the past five years. This marked an 8 percentage point increase compared to May 2024, reinforcing wind’s role as the backbone of Britain’s clean energy supply. Gas, on the other hand, accounted for just 20% of the electricity mix, down 5 percentage points from May 2024 and its lowest May contribution in five years. Notably, gas generation in May 2025 was half of that in May 2021, signalling measurable progress in reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Nuclear power contributed 15% to the mix, a figure that has remained relatively stable in recent years. While slightly below the 17% share seen in May 2022 and 2024, it matches contributions in May 2021 and 2023, reflecting a continued but stagnant role in the generation mix. Solar generation rose significantly, climbing 4 percentage points year-on-year to reach 12%, its highest May contribution in the last five years. This growth underscores solar’s expanding role in supporting seasonal energy demand. Biomass remained consistent, supplying 7% of Britain's electricity in May 2025, in line with its contribution in May 2024. Hydropower also maintained a consistent presence at 1%, though this was below the 2% observed in May 2022. Electricity imports fell slightly to 17%, down from 19% in May 2024, but still substantially above the 2% recorded in May 2022. Meanwhile, storage technologies contributed 2%, marking their highest May share in the last five years and reflecting incremental progress in energy flexibility. Coal remained absent from the generation mix in May 2025, following its complete phase-out from the grid. Zero-Carbon Sources & Carbon Intensity Zero-carbon sources, including wind, solar, nuclear, and hydro, delivered 57% of Britain’s electricity in May 2025, the highest May share in recent years and a 12 percentage point increase from May 2024. This boost in clean generation contributed to a notable reduction in carbon intensity, which fell to 106 gCO₂/kWh, 15% lower than the previous year. In longer terms, the 12-month rolling average for zero-carbon generation reached 50%, up 1% from April’s update but still 1% below the level seen one year earlier. In contrast, the rolling average carbon intensity sits at 129 gCO₂/kWh, the lowest level of the past five years, indicating gradual improvement despite short-term fluctuations. Concluding Remarks May 2025 saw a strong rebound in wind and solar generation, helping to push zero-carbon sources to their highest May share in recent years and driving carbon intensity to new lows. The continued decline in gas and the absence of coal signal real progress, although the stability of nuclear, combined with limited hydro output and a marginal decline in the 12-month rolling average energy generation from zero-carbon sources, highlight the importance of accelerating renewable deployment to maintain momentum. With imports still high and storage only beginning to scale, the data points to both achievements and remaining vulnerabilities. To ensure long-term resilience and carbon reduction, sustained investment in domestic renewables and flexible technologies will be essential. Britain's Electricity Summary Charts

As energy prices climb, staff costs rise, and local authority budgets tighten, leisure centres across the UK are navigating choppy waters. Nowhere is this pressure felt more acutely than in facilities with swimming pools. These highly valued public assets are also among the most energy-intensive parts of any leisure operation, with heating, ventilation, water treatment, pumps and lighting systems operating almost constantly. According to a Lords report, between 2021 and 2024, 77 local authority managed leisure centres across the UK closed, many citing increases in utility costs as a contributing factor. In 2023, a medium sized operator of public leisure centres announced that it's utility costs had increased from £8m in 2021 to an estimated £24m in 2024. Yet, despite these pressures, swimming pools remain a vital part of the health and wellbeing infrastructure in our communities. The challenge is to safeguard their future by reducing operational costs and environmental impact while maintaining, or ideally improving, comfort and safety for bathers. This is where a focused, evidence-led approach to energy efficiency becomes not just a sustainability initiative, but a financial and operational necessity. Understanding the Challenges Operators of swimming pools in the public and private sectors are facing a perfect storm: Rising utility costs : Volatile energy markets and increasing wholesale prices mean that the cost of running a pool is often the single largest line item in an operator's budget. Ageing infrastructure : Many leisure centres were built decades ago, with plant and building fabric now well beyond their optimal design life. Staffing pressures : Increased employer National Insurance contributions, inflationary wage growth, and recruitment challenges in technical and operations roles strain budgets further. Local authority cuts : For council-run sites or those operated under local authority contracts, budget reductions mean less funding for capital improvements, making it harder to invest in long-term savings. In this environment, energy efficiency isn't just about sustainability; it is core to financial survival. Ten Focus Areas for Energy Efficiency in Swimming Pool Operations edenseven have worked with a wide range of leisure operators across the UK, from large national chains, local authority and privately run leisure centres and single-site independents. While every facility is unique, there are ten consistent focus areas that can help reduce costs and improve user experience. 1. Pool Hall Air Handling Systems Air handling units (AHUs) that serve the pool hall are often some of the most energy-intensive pieces of equipment in a leisure centre. Retrofitting systems with high-efficiency heat recovery, variable speed fans, and improved controls can yield significant savings. Maintaining optimal humidity and air temperature also reduces condensation and improves comfort and reduces building degradation. 2. Pool Water Heating and Temperature Management Upgrading boiler systems or integrating renewable sources such as heat pumps can drastically reduce energy usage. Modern controls, temperature stratification management, and insulation of pipework all contribute to system efficiency. Managing water temperatures to an optimal level reduces the need for backwashing. Higher pool water temperatures lead to increased microbiological growth and a higher need for backwashing and chemical dosing. 3. Lighting Efficiency LED lighting retrofits, particularly in pool halls and plant rooms, provide rapid returns on investment. Coupled with intelligent lighting controls (e.g., occupancy sensors in changing villages and toilets, and daylight dimming), this can lower costs while enhancing visibility and safety. 4. Building Fabric and Insulation Improved insulation of walls, roofs, and glazing can reduce heat loss, especially in pool halls where thermal demand is constant. Draught-proofing and maintenance of seals around windows and doors are low-cost measures that can have a noticeable impact. 5. Water Treatment System and Backwash Optimisation Advancements in filtration and chemical water treatment technologies, such as glass-media filtration and UV treatment, can reduce the need for chemical dosing and water changes. Smart controls help optimise chemical usage, water balance, and backwash schedules, lowering energy and water consumption. 6. Pool Covers and Evaporation Management Heat loss due to evaporation is one of the largest energy drains in any pool. High-quality, well-fitted pool covers can reduce overnight losses dramatically. Automatic covers also improve usability and safety. Consideration should be given to using surplus heat from other parts of the operation or other local businesses if possible - data centres or industrial processes could prove to be ideal partners. 7. Smart Controls and Building Management Systems (BMS) Many leisure centres are under-utilising their existing BMS or lack one altogether. Integrating systems and enabling real-time monitoring and automated control can unlock both energy and operational efficiencies. 8. Renewable and Low Carbon Technologies On-site solar PV, air or ground source heat pumps, and battery storage can help offset rising energy prices. While capital intensive, these measures may qualify for grant support or financing options that align with local authority decarbonisation plans. 9. Staff Training and Customer Engagement Empowering staff with energy awareness training and involving them in optimisation routines often leads to behavioural changes that enhance the impact of technical interventions. From plant operators to lifeguards, everyone has a role to play. Engaging with customers to shower before using the pool reduces biological loading and the need for chemicals and backwashing, saving water, energy and chemicals. 10. Data Monitoring and Continuous Improvement You can't manage what you don't measure. Installing sub-metering, using analytics platforms like cero.earth, and setting performance benchmarks allows leisure centre operators to track progress and target interventions more precisely. This data-led approach drives accountability and long-term success. Planning the Journey: From Audit to Action There is no one-size fits all solution, but there is a process. Most successful transformations start with a detailed energy and plant condition audit, tailored to the unique operational profile of the site. From here, a prioritised action plan can be developed, balancing short-term wins with longer-term investments. Understanding funding routes for public sector managed facilities is also critical. Many operators overlook opportunities for central government or local authority-backed capital funding. Our team has supported clients in identifying and securing funding through schemes such as the Public Sector Decarbonisation Scheme and local net-zero initiatives. Crucially, implementation must be done in a way that minimises disruption to operations and maintains health and safety standards. That means working closely with operational staff, technical teams, and supply chains. A Sustainable Future for Swimming At edenseven we believe that every leisure centre and swimming pool in the UK can be part of a more sustainable future, one where communities continue to benefit from the physical and mental wellbeing that swimming pools and leisure centre facilities offer, without shouldering unsustainable costs. Our role as a sustainability consultancy is not to offer off-the-shelf solutions, but to partner with clients to understand their context, build the right roadmap, and support delivery at every stage. From strategic advice and audits, through to technical specification and project management, our credibility is built on a track record of helping leisure operators navigate these exact challenges. If you are responsible for a facility that includes a swimming pool, now is the time to act, come and talk to us . Rising costs are unlikely to reverse themselves, but with the right expertise and a structured approach, they can be managed and even turned into opportunities to improve performance and bather comfort, engage with you customers and improve your leisure centre’s environmental impact.

Managing Partner, Pete Nisbet, explains more: Over 80% of consumers say they're willing to pay more for sustainable products. But here’s the catch: trust is fragile . Too many claims are vague, inconsistent, or unverifiable. And consumers are noticing. Greenwashing isn’t just a PR problem, it’s a business risk. Transparency and accountability are no longer optional. Credible data, third-party verification, and measurable outcomes are essential. They don’t just protect you, they future-proof your business. Because once trust is broken, it’s hard to rebuild. Over half of consumers say they’d stop buying from brands they believe mislead on sustainability. That’s not just reputational damage, it’s lost customers, investment, and talent. Why does this matter? For People: When companies walk the talk, people benefit through better working conditions, local job creation, and access to more ethical, healthier products. Trust builds loyalty. Transparent, credible action forges stronger relationships between businesses and the people they serve. For Profit: Sustainability isn’t a cost, it’s a growth strategy. Sustainable products grew 2.7x faster than conventional ones between 2015 & 2019. Over $30 trillion is now invested in ESG assets, and is expected to reach $40 trillion by 2030. For the Planet: The climate crisis is happening now. We need bold, credible action, not just pledges. Science-based targets, circular design, and effective net-zero strategies are essential. Turning Ambition into Action: At edenseven, we design, build, and implement sustainability strategies that deliver. We consistently see these benefits for the clients we work with: reducing costs, proving impact to customers and investors, and cutting regulatory risk. Most importantly, we help minimise your impact on the planet. If you want to see how much of an impact we can make for your business, send us a message! We’ll help you turn genuine sustainability efforts into clear, credible results that future-proof your business and resonate with your customers & key stakeholders.

Fuel Type Breakdown Britain’s electricity generation in April 2025 saw a notable shift, with gas reclaiming its position as the leading source of electricity generation. Contributing 26% of the energy mix, gas usage rose by nearly 10 percentage points compared to April 2024. Despite this, gas consumption remained below levels seen in April 2021, 2022, and 2023. The rise in gas was largely a response to a substantial drop in wind energy generation, which fell by more than 10 percentage points year-on-year to 22%. This was wind’s second-lowest April contribution in the last five years. The shortfall in wind output played a critical role in driving up reliance on fossil fuels, undermining progress toward a cleaner energy mix. Likely as a result of favourable weather conditions, solar generation rose sharply, from 6% in April 2024 to 11% in April 2025. This marks its highest April contribution in five years and highlights solar’s growing potential in Britain’s energy transition. Conversely, nuclear power continued to decline, contributing just 14% to the electricity mix, down from 16% the previous year and its lowest April share in half a decade. The consistent drop in nuclear output, coupled with weak wind performance, placed additional pressure on other sources to fill the gap. Biomass remained stable at 7%, matching its highest April contribution in the last five years, while hydropower fell slightly to 1%. Together, these sources provided limited compensation for the downturn in wind and nuclear output. Coal contributed 0%, following its complete phase-out in September 2024. For context, coal had still accounted for 1% of electricity generation in April 2024. Electricity imports increased by 3 percentage points to 18%, the highest April share in five years, suggesting growing reliance on cross-border supply to maintain grid stability. Similarly, storage technologies contributed 2% to the mix, their highest April level to date, signaling incremental progress in energy flexibility and resilience. Zero-Carbon Sources & Carbon Intensity Zero-carbon sources, comprising wind, solar, nuclear, hydro accounted for 46% of electricity generation in April 2025. This represented a 13% decline from April 2024, and was accompanied by a sharp rise in carbon intensity to 133 gCO₂/kWh, a 45% year-on-year increase. Over a longer timeframe, the 12-month rolling average for zero-carbon generation stood at 49%, down 2% from the previous year. Meanwhile, the 12-month rolling average carbon intensity stood at 131 gCO₂/kWh, only 8% lower than the year before and a sharp contrast to the 22% year-on-year reduction recorded ju st six months earlier in October 2024. This underscores a concerning stagnation in Britain’s clean energy momentum. Concluding Remarks April's mixed performance highlights a concerning slowdown in Britain's progress towards a decarbonised energy grid. The decline in the share of renewables over the last 12-months, coupled with only an 8% year-on-year reduction in carbon intensity, highlights a loss of momentum in decarbonising the grid. While the increased supply from solar and storage is a positive development, the decline in wind, nuclear and hyrdo is concerning. Although wind's decline may reflect temporary weather conditions, the broader trend signals an urgent need to ramp up investment into renewables. To restore progress toward a resilient, net zero power system and reduce dependence on imports, Britain must accelerate the deployment of renewables and strengthen its commitment to long-term energy security. Britain's Electricity Summary Charts

Fuel Type Breakdown In March 2025, gas was the leading source of Britain's electricity generation, contributing 31% of the energy mix, a 7% increase from March 2024. However, this was the second-lowest gas share for March in the last five years. Wind energy accounted for 26%, down 7% from March 2024. Solar contributed 7%, up 3% year-on-year, it's highest contribution for March in the previous five years. Hydro and storage maintained consistent contributions of 3% and 1%, respectively, matching their performance for every March in the last five years. Biomass contributed 5%, the same as March 2024; however, 3% below it's share in March 2021. Coal contributed 0%, following its phase-out in September 2024. For comparison, coal made up 1% of the mix in March 2024. Zero-Carbon Sources & Carbon Intensity Zero-carbon sources delivered 45% of Britain's electricity in March 2025 - 6% lower than March 2024 and the second-lowest March share in the past five years. This decline led to a higher carbon intensity, with emissions at 146 gCO₂/kWh, up 15% from March 2024. The rolling 12-month average for zero-carbon electricity remained at 50%, unchanged from the previous period, indicating stagnation in renewable integration. However, carbon intensity over this 12-month period continues to be the lowest of the past five years, at 127 gCO₂/kWh, and 14% lower than the previous 12-month period. Increasing renewable electricity generation remains crucial to achieving net-zero goals, enhancing energy security, and reducing reliance on imports. Britain's Electricity Summary Charts

edenseven are following trends in the renewable energy sector closely, as decarbonising the energy sector is vital for ensuring a sustainable future and achieving Net Zero. Considering the recent DESNZ quarterly update of the renewable energy planning database, we have produced a consolidated summary of projects in the United Kingdom that have received planning permission. We will continue to release updates each quarter. INSIGHT In 2024, the UK approved 592 solar PV projects , the third-highest of any year in the last 15 years. However, the energy capacity expected to be delivered by these projects is 24% lower than in 2023. 2024 ranked 11th out of the last 15 years for the total number of onshore wind projects granted planning permission. These projects will deliver the lowest energy capacity for onshore wind approved for any year in the last 15 years, and is down 59% year-on-year. Energy capacity from offshore wind projects granted planning permission in 2024 saw a 62% drop compared to 2023, despite the same number of projects being approved as the prior year. Overall, the total approved renewable energy capacity from wind and solar projects dropped by 43% compared to 2023 , with offshore wind seeing the steepest decline. However, the average capacity per solar PV project increased by 50% , while onshore and offshore wind saw reductions of 63% and 62% , respectively. These findings suggest that we are not implementing wind and solar renewable energy projects quickly enough in the UK to achieve a decarbonised energy network by 2030.

In February 2025, gas accounted for 33% of Britain’s electricity mix, making it the largest contributor, slightly ahead of wind energy, which supplied 32%. This marks a 6% increase in gas-generated electricity and a 3% decline in wind energy compared to February 2024. The highest-ever wind energy contribution for February was recorded in 2022, when it made up 40% of Britain's electricity mix. Solar, biomass, and storage delivered the same contributions as in February 2024, contributing 2%, 7% and 1% respectively. Nuclear energy saw a 1% increase, supplying 12% of Britain's electricity in February 2025 - its highest share for February in the past three years. However, this remains 2% below the levels recorded in February 2021 and 2022. Hydro contributed 2% of Britain’s electricity generation, a 1% decrease from its 3% share in February 2024. Coal, which was phased out of UK electricity generation in September 2024, contributed 0% in February 2025. For comparison, coal accounted for 1% of electricity generation in February 2024. Zero-carbon sources delivered 48% of Britain’s electricity in February 2025, 3% lower than in February 2024 and the third highest for February in the last five years. However, the rolling 12-month average for zero-carbon electricity remains at 50%, the highest of the past five years. The carbon intensity of electricity generation in February 2025 was 147 gCO₂/kWh, 11% higher than in February 2024 and the third highest of the last five years. Despite this, the rolling 12-month average carbon intensity stands at 126 gCO₂/kWh, the lowest in five years and 17% lower than the previous 12-month period. Increasing renewable electricity generation remains crucial to achieving net-zero goals, enhancing energy security, and reducing reliance on imports.

On March 5th, 2025, Sustainability and FM Leaders captured the attention of Business Directors. By signing their Energy Savings Opportunity Scheme (ESOS) Action Plans, they collectively endorsed a strong business case with tangible opportunities to reduce energy consumption and costs, all in preparation for the reporting period ending on December 5th, 2027. Few businesses would dispute the benefits of focusing on energy efficiency. It not only reduces operational costs and enhances profitability but also contributes to decarbonisation efforts - an increasingly important factor for sustainability-conscious employees, customers, and shareholders. Time to Unlock Savings From Your List of ESOS Measures As part of Phase 3, approximately 11,900 UK businesses submitted their ESOS reports in August 2024. These were followed by the required Action Plans on March 5th, 2025. Moving forward, businesses must submit annual progress reports in the final Phase 4 assessment on the December 5th, 2027. The latest government guidance indicates that, instead of using the ESOS portal, companies subject to SECR may "report progress annually via the energy efficiency narrative section in SECR reports." (This flexibility depends on parliamentary time and scrutiny). Regardless of the method, demonstrating effective management of the Action Plan’s implementation is both a regulatory requirement and a best practice." A Business Case Approach to Prioritise Interventions edenseven's extensive experience in supporting customers with ESOS compliance has been overwhelmingly positive. Businesses were given the opportunity to tailor their energy-saving actions to align with their unique needs and strategies. Notably, ESOS guidance doesn't mandate a minimum number of Measures in the Action Plan. However, there is a hint of a reputational impact from September 2025, when the Environment Agency will publish action plans, including of companies that have not committed to any Measure. A well-structured action plan can significantly enhance a company's credibility. Businesses have the flexibility to choose energy-saving initiatives that align with their specific needs, considering factors such as budget, lifecycle assessments, estate strategy, and fleet procurement cycles. By thoughtfully balancing these considerations with broader sustainability goals, companies can achieve meaningful progress while maintaining financial and operational stability. Expertise and Tools to Make it Happen in Phase 4 With Phase 4 of ESOS now fully underway, meticulous planning and well-supported investment decisions are essential. Companies must build robust business cases that integrate technical, regulatory, and financial considerations. In response to this need, edenseven has advanced its cero.earth carbon accounting & management platform by introducing a dynamic Project Forecasting and Management module. Project Forecasting and Management Module cero.earth ’s project tools serve as a comprehensive database of all potential projects, enabling real-time impact analysis, including: Cost and savings projections CO2 emissions reductions Energy Use Intensity improvements These tools enable businesses to forecast the financial costs and benefits of their approved measures within an agreed timeframe. For example, a CFO can review scenario options that highlight the financial and environmental advantages of initiatives such as HVAC retrofitting, solar PV installation, or even building decommissioning. Monitoring Energy Performance for ESOS Requirement Together with SECR Reporting cero.earth is already configured to automatically generate Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) reports. While the Environment Agency has outlined the content expectations for the December 2025 progress update, formatting requirements remain unspecified. edenseven remains agile in supporting customers with both insights and tools to streamline their reporting. Prepare for the Future with edenseven The transition to a more sustainable business model requires proactive planning and strategic execution. Get in touch today to learn how edenseven can support your journey towards compliance and sustainability excellence.



